|
此版本仍在开发中,尚未被视为稳定版本。对于最新的稳定版本,请使用 Spring Security 6.4.1! |
授权架构
本节描述了适用于授权的 Spring Security 体系结构。
当局
Authentication讨论所有Authenticationimplementations 存储一个GrantedAuthority对象。
这些权限表示已授予委托人的权限。
这GrantedAuthority对象将插入到Authenticationobject 的AuthenticationManager,稍后由AccessDecisionManager实例。
这GrantedAuthorityinterface 只有一个方法:
String getAuthority();此方法由AuthorizationManager实例来获取精确的String表示GrantedAuthority.
通过将表示形式作为String一个GrantedAuthority大多数人都可以轻松“阅读”AuthorizationManager实现。
如果GrantedAuthority不能精确地表示为String这GrantedAuthority被视为“复杂”,并且getAuthority()必须返回null.
综合体示例GrantedAuthority将是一个实现,用于存储适用于不同客户账号的作和权限阈值列表。
代表这个综合体GrantedAuthority作为String会相当困难。因此,getAuthority()method 应返回null.
这向任何AuthorizationManager它需要支持特定的GrantedAuthority实现来理解其内容。
Spring Security 包括一个具体的GrantedAuthority实现:SimpleGrantedAuthority.
此实现允许任何用户指定的String转换为GrantedAuthority.
都AuthenticationProvider安全架构中包含的实例使用SimpleGrantedAuthority要填充Authentication对象。
您可以使用GrantedAuthorityDefaults.GrantedAuthorityDefaults存在以允许自定义用于基于角色的授权规则的前缀。
您可以通过公开GrantedAuthorityDefaultsbean,如下所示:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
-
Xml
@Bean
static GrantedAuthorityDefaults grantedAuthorityDefaults() {
return new GrantedAuthorityDefaults("MYPREFIX_");
}companion object {
@Bean
fun grantedAuthorityDefaults() : GrantedAuthorityDefaults {
return GrantedAuthorityDefaults("MYPREFIX_");
}
}<bean id="grantedAuthorityDefaults" class="org.springframework.security.config.core.GrantedAuthorityDefaults">
<constructor-arg value="MYPREFIX_"/>
</bean>|
您暴露 |
调用处理
Spring Security 提供了拦截器,用于控制对安全对象的访问,例如方法调用或 Web 请求。
关于是否允许继续调用的调用前决定由AuthorizationManager实例。
此外,关于是否可以返回给定值的调用后决定由AuthorizationManager实例。
The AuthorizationManager
AuthorizationManager取代两者AccessDecisionManager和AccessDecisionVoter.
自定义AccessDecisionManager或AccessDecisionVoter鼓励更改为使用AuthorizationManager.
AuthorizationManager由 Spring Security 的基于请求、基于方法和基于消息的授权组件调用,并负责做出最终的访问控制决策。
这AuthorizationManagerinterface 包含两个方法:
AuthorizationDecision check(Supplier<Authentication> authentication, Object secureObject);
default void verify(Supplier<Authentication> authentication, Object secureObject)
throws AccessDeniedException {
// ...
}这AuthorizationManager的check方法传递它所需的所有相关信息,以便做出授权决策。
特别是,将安全的Object允许检查实际安全对象调用中包含的那些参数。
例如,假设安全对象是一个MethodInvocation.
查询MethodInvocation对于任何Customer参数,然后在AuthorizationManager以确保允许 Principal 对该客户进行作。
实现应返回正AuthorizationDecision如果授予访问权限,则为负数AuthorizationDecision如果访问被拒绝,并且 nullAuthorizationDecision当放弃做决定时。
verify调用check并随后抛出一个AccessDeniedException如果出现负数AuthorizationDecision.
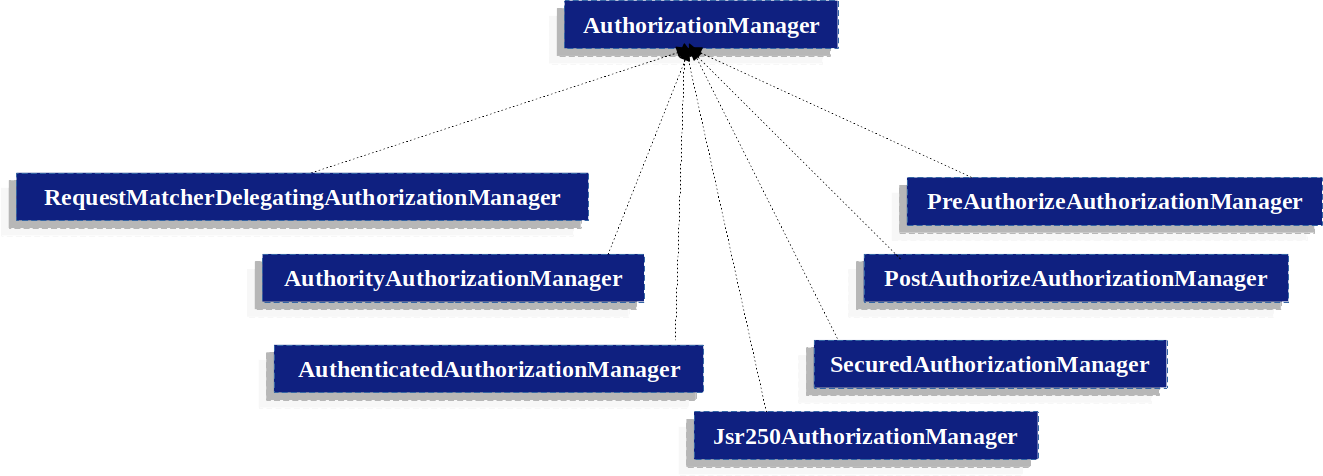
基于委托的 AuthorizationManager 实现
虽然用户可以实现自己的AuthorizationManager为了控制授权的所有方面,Spring Security 附带了一个委托AuthorizationManager可以与个人协作AuthorizationManagers.
RequestMatcherDelegatingAuthorizationManager将请求与最合适的委托人匹配AuthorizationManager.
为了方法安全性,您可以使用AuthorizationManagerBeforeMethodInterceptor和AuthorizationManagerAfterMethodInterceptor.
授权管理器实现说明了相关的类。
使用这种方法,将AuthorizationManager可以在授权决策时轮询 implementations。
权限授权管理器
最常见的AuthorizationManager与 Spring Security 一起提供的是AuthorityAuthorizationManager.
它配置了一组给定的权限,以在当前的Authentication.
它将返回正值AuthorizationDecision如果Authentication包含任何已配置的权限。
它将返回一个负数AuthorizationDecision否则。
已验证的授权管理器
另一个 Manager 是AuthenticatedAuthorizationManager.
它可用于区分匿名用户、完全身份验证用户和经过记住我身份验证的用户。
许多站点允许在 remember-me 身份验证下进行某些受限访问,但需要用户通过登录来确认其身份才能获得完全访问权限。
授权管理器
中还有一些有用的静态工厂AuthorizationManagers用于撰写个人AuthorizationManagers 转换为更复杂的表达式。
自定义授权管理器
显然,您还可以实现自定义AuthorizationManager而且你几乎可以在其中放置任何你想要的访问控制逻辑。
它可能特定于您的应用程序 (与业务逻辑相关),或者它可能实现一些安全管理逻辑。
例如,您可以创建可以查询 Open Policy Agent 或您自己的授权数据库的实现。
您可以在 Spring 网站上找到一篇博客文章,其中描述了如何使用 legacyAccessDecisionVoter实时拒绝账户被暂停的用户访问。
您可以通过实施来实现相同的结果AuthorizationManager相反。 |
调整 AccessDecisionManager 和 AccessDecisionVoters
上一页AuthorizationManager,Spring Security 发布AccessDecisionManager和AccessDecisionVoter.
在某些情况下,例如迁移较旧的应用程序,可能需要引入AuthorizationManager这会调用AccessDecisionManager或AccessDecisionVoter.
调用现有的AccessDecisionManager,您可以执行以下作:
-
Java
@Component
public class AccessDecisionManagerAuthorizationManagerAdapter implements AuthorizationManager {
private final AccessDecisionManager accessDecisionManager;
private final SecurityMetadataSource securityMetadataSource;
@Override
public AuthorizationDecision check(Supplier<Authentication> authentication, Object object) {
try {
Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes = this.securityMetadataSource.getAttributes(object);
this.accessDecisionManager.decide(authentication.get(), object, attributes);
return new AuthorizationDecision(true);
} catch (AccessDeniedException ex) {
return new AuthorizationDecision(false);
}
}
@Override
public void verify(Supplier<Authentication> authentication, Object object) {
Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes = this.securityMetadataSource.getAttributes(object);
this.accessDecisionManager.decide(authentication.get(), object, attributes);
}
}然后将其连接到您的SecurityFilterChain.
或者只调用AccessDecisionVoter,您可以执行以下作:
-
Java
@Component
public class AccessDecisionVoterAuthorizationManagerAdapter implements AuthorizationManager {
private final AccessDecisionVoter accessDecisionVoter;
private final SecurityMetadataSource securityMetadataSource;
@Override
public AuthorizationDecision check(Supplier<Authentication> authentication, Object object) {
Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes = this.securityMetadataSource.getAttributes(object);
int decision = this.accessDecisionVoter.vote(authentication.get(), object, attributes);
switch (decision) {
case ACCESS_GRANTED:
return new AuthorizationDecision(true);
case ACCESS_DENIED:
return new AuthorizationDecision(false);
}
return null;
}
}然后将其连接到您的SecurityFilterChain.
分层角色
一个常见的要求是,应用程序中的特定角色应该自动 “包含” 其他角色。 例如,在具有 “admin” 和 “user” 角色概念的应用程序中,您可能希望 admin 能够执行普通用户可以执行的所有作。 为此,您可以确保所有管理员用户也都分配了 “user” 角色。 或者,您可以修改每个访问约束,这要求 “user” 角色也包括 “admin” 角色。 如果您的应用程序中有很多不同的角色,这可能会变得相当复杂。
使用 role-hierarchy 允许您配置哪些角色(或权限)应包含其他角色。
基于筛选条件的授权支持此功能HttpSecurity#authorizeHttpRequests对于基于方法的授权,通过DefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandler对于 pre-post 注释,SecuredAuthorizationManager为@Secured和Jsr250AuthorizationManager以获取 JSR-250 注释。
您可以通过以下方式同时为所有这些应用程序配置行为:
-
Java
-
Xml
@Bean
static RoleHierarchy roleHierarchy() {
return RoleHierarchyImpl.withDefaultRolePrefix()
.role("ADMIN").implies("STAFF")
.role("STAFF").implies("USER")
.role("USER").implies("GUEST")
.build();
}
// and, if using pre-post method security also add
@Bean
static MethodSecurityExpressionHandler methodSecurityExpressionHandler(RoleHierarchy roleHierarchy) {
DefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandler expressionHandler = new DefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandler();
expressionHandler.setRoleHierarchy(roleHierarchy);
return expressionHandler;
}<bean id="roleHierarchy"
class="org.springframework.security.access.hierarchicalroles.RoleHierarchyImpl" factory-method="fromHierarchy">
<constructor-arg>
<value>
ROLE_ADMIN > ROLE_STAFF
ROLE_STAFF > ROLE_USER
ROLE_USER > ROLE_GUEST
</value>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!-- and, if using method security also add -->
<bean id="methodSecurityExpressionHandler"
class="org.springframework.security.access.expression.method.MethodSecurityExpressionHandler">
<property ref="roleHierarchy"/>
</bean>这里我们在层次结构中有四个角色ROLE_ADMIN ⇒ ROLE_STAFF ⇒ ROLE_USER ⇒ ROLE_GUEST.
通过ROLE_ADMIN)的行为将表现得好像它们具有所有四个角色时,根据任何基于过滤器或方法的规则评估安全约束。
该符号可以被认为是“包含”的意思。> |
角色层次结构提供了一种简便的方法,可以简化应用程序的访问控制配置数据和/或减少需要分配给用户的权限数量。 对于更复杂的要求,您可能希望在应用程序所需的特定访问权限和分配给用户的角色之间定义一个逻辑映射,并在加载用户信息时在两者之间进行转换。
旧版授权组件
| Spring Security 包含一些旧组件。 由于它们尚未删除,因此包含文档以用于历史目的。 他们推荐的替代品如上所述。 |
The AccessDecisionManager
这AccessDecisionManager由AbstractSecurityInterceptor并负责做出最终的访问控制决策。
这AccessDecisionManagerinterface 包含三种方法:
void decide(Authentication authentication, Object secureObject,
Collection<ConfigAttribute> attrs) throws AccessDeniedException;
boolean supports(ConfigAttribute attribute);
boolean supports(Class clazz);这decide方法AccessDecisionManager传递做出授权决策所需的所有相关信息。
特别是,将安全的Object用于检查实际安全对象调用中包含的那些参数。
例如,假设安全对象是MethodInvocation.
您可以查询MethodInvocation对于任何Customer参数,然后在AccessDecisionManager以确保允许 Principal 对该客户进行作。
实现应抛出AccessDeniedException如果访问被拒绝。
这supports(ConfigAttribute)方法由AbstractSecurityInterceptor以确定AccessDecisionManager可以处理传递的ConfigAttribute.
这supports(Class)方法,以确保配置的AccessDecisionManager支持安全侦听器提供的安全对象的类型。
基于投票的 AccessDecisionManager 实现
虽然用户可以实现自己的AccessDecisionManager为了控制授权的所有方面,Spring Security 包括多个AccessDecisionManager基于 vote 的实现。Voting Decision Manager 描述了相关的类。
下图显示了AccessDecisionManager接口:
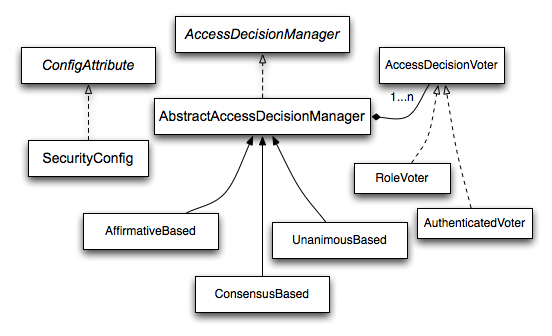
通过使用这种方法,一系列AccessDecisionVoter实施在授权决策时进行轮询。
这AccessDecisionManager然后决定是否抛出AccessDeniedException根据其对选票的评估。
这AccessDecisionVoterinterface 有三种方法:
int vote(Authentication authentication, Object object, Collection<ConfigAttribute> attrs);
boolean supports(ConfigAttribute attribute);
boolean supports(Class clazz);具体实现返回一个int,可能的值将反映在AccessDecisionVoter名为 static 字段ACCESS_ABSTAIN,ACCESS_DENIED和ACCESS_GRANTED.
投票实现返回ACCESS_ABSTAIN如果它对授权决定没有意见。
如果它确实有观点,则必须返回ACCESS_DENIED或ACCESS_GRANTED.
有三种具体AccessDecisionManager实现来统计选票。
这ConsensusBasedimplementation 根据非弃权票的共识授予或拒绝访问权限。
提供属性以控制在票数相等或所有投票都弃权的情况下的行为。
这AffirmativeBasedimplementation 在一个或多个ACCESS_GRANTED已收到投票(换句话说,如果至少有一个 GRANT 投票,则 DENY 投票将被忽略)。
与ConsensusBasedimplementation 中,有一个参数控制所有选民弃权时的行为。
这UnanimousBased提供商期望 UnanimousACCESS_GRANTED投票以授予访问权限,忽略弃权。
如果存在任何访问权限,它会拒绝访问ACCESS_DENIED投票。
与其他实现一样,有一个参数控制所有选民弃权时的行为。
您可以实现自定义AccessDecisionManager这以不同的方式计算选票。
例如,来自特定AccessDecisionVoter可能会获得额外的权重,而来自特定选民的拒绝投票可能具有否决权。
角色投票者
最常用的AccessDecisionVoter随 Spring Security 一起提供的是RoleVoter,它将配置属性视为角色名称,如果已为用户分配了该角色,则投票授予访问权限。
如果有的话,它会投票ConfigAttribute以ROLE_前缀。
如果存在GrantedAuthority返回一个String表示形式(来自getAuthority()方法)正好等于一个或多个ConfigAttributes以ROLE_前缀。
如果没有任何ConfigAttribute起始于ROLE_,RoleVotervotes 拒绝访问。
如果没有ConfigAttribute开头为ROLE_,则选民弃权。
已验证的选民
我们隐晦地看到的另一个投票者是AuthenticatedVoter,该 ID 可用于区分匿名用户、经过完全身份验证的用户和经过 Remember me 身份验证的用户。
许多站点允许在 remember-me 身份验证下进行某些受限访问,但需要用户通过登录来确认其身份才能获得完全访问权限。
当我们使用IS_AUTHENTICATED_ANONYMOUSLY属性来授予匿名访问权限,则此属性由AuthenticatedVoter.
有关更多信息,请参阅AuthenticatedVoter.
自定义选民
您还可以实现自定义AccessDecisionVoter并在其中放置几乎任何您想要的访问控制逻辑。
它可能特定于您的应用程序 (与业务逻辑相关),或者它可能实现一些安全管理逻辑。
例如,在 Spring Web 站点上,您可以找到一篇博客文章,其中介绍了如何使用投票者实时拒绝帐户已被暂停的用户的访问。
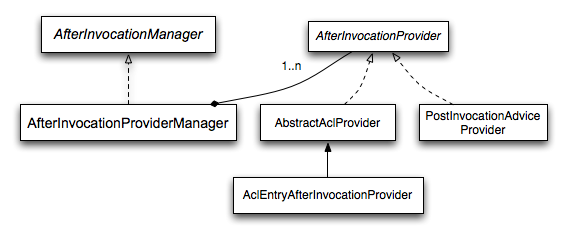
与 Spring Security 的许多其他部分一样,AfterInvocationManager具有单个具体实现,AfterInvocationProviderManager,它会轮询AfterInvocationProviders.
每AfterInvocationProvider可以修改 return 对象或抛出AccessDeniedException.
事实上,多个提供程序可以修改对象,因为前一个提供程序的结果会传递给列表中的下一个提供程序。
请注意,如果您使用的是AfterInvocationManager,您仍然需要允许MethodSecurityInterceptor的AccessDecisionManager以允许作。
如果您使用的是典型的 Spring Security 包括AccessDecisionManager实现中,如果没有为特定的安全方法调用定义配置属性,将导致每个AccessDecisionVoter弃权。
反过来,如果AccessDecisionManager属性 “allowIfAllAbstainDecisions” 为false一AccessDeniedException将被抛出。
您可以通过 (i) 将 “allowIfAllAbstainDecisions” 设置为true(尽管通常不建议这样做)或 (ii) 只需确保至少有一个配置属性AccessDecisionVoter将投票授予访问权限。
后一种(推荐)方法通常是通过ROLE_USER或ROLE_AUTHENTICATEDconfiguration 属性。