|
此版本仍在开发中,尚未被视为稳定版本。对于最新的稳定版本,请使用 Spring Security 6.4.3! |
使用 AuthorizationFilter 授权 HttpServletRequests
本节以 Servlet 体系结构和实现为基础,深入探讨了授权在基于 Servlet 的应用程序中的工作原理。
AuthorizationFilter取代FilterSecurityInterceptor.
为了保持向后兼容,FilterSecurityInterceptor仍然是默认值。
本节讨论如何AuthorizationFilter有效以及如何覆盖默认配置。 |
这AuthorizationFilter提供HttpServletRequests.
它作为 Security Filters 之一插入到 FilterChainProxy 中。
您可以在声明SecurityFilterChain.
而不是使用authorizeRequests用authorizeHttpRequests这样:
-
Java
@Bean
SecurityFilterChain web(HttpSecurity http) throws AuthenticationException {
http
.authorizeHttpRequests((authorize) -> authorize
.anyRequest().authenticated();
)
// ...
return http.build();
}这改进了authorizeRequests以多种方式:
-
使用简化的
AuthorizationManagerAPI 而不是元数据源、配置属性、决策管理器和投票者。 这简化了重用和定制。 -
延误
Authentication查找。 它不需要为每个请求查找身份验证,而只会在授权决策需要身份验证的请求中查找身份验证。 -
基于 Bean 的配置支持。
什么时候authorizeHttpRequests替换为authorizeRequests然后AuthorizationFilter替换为FilterSecurityInterceptor.
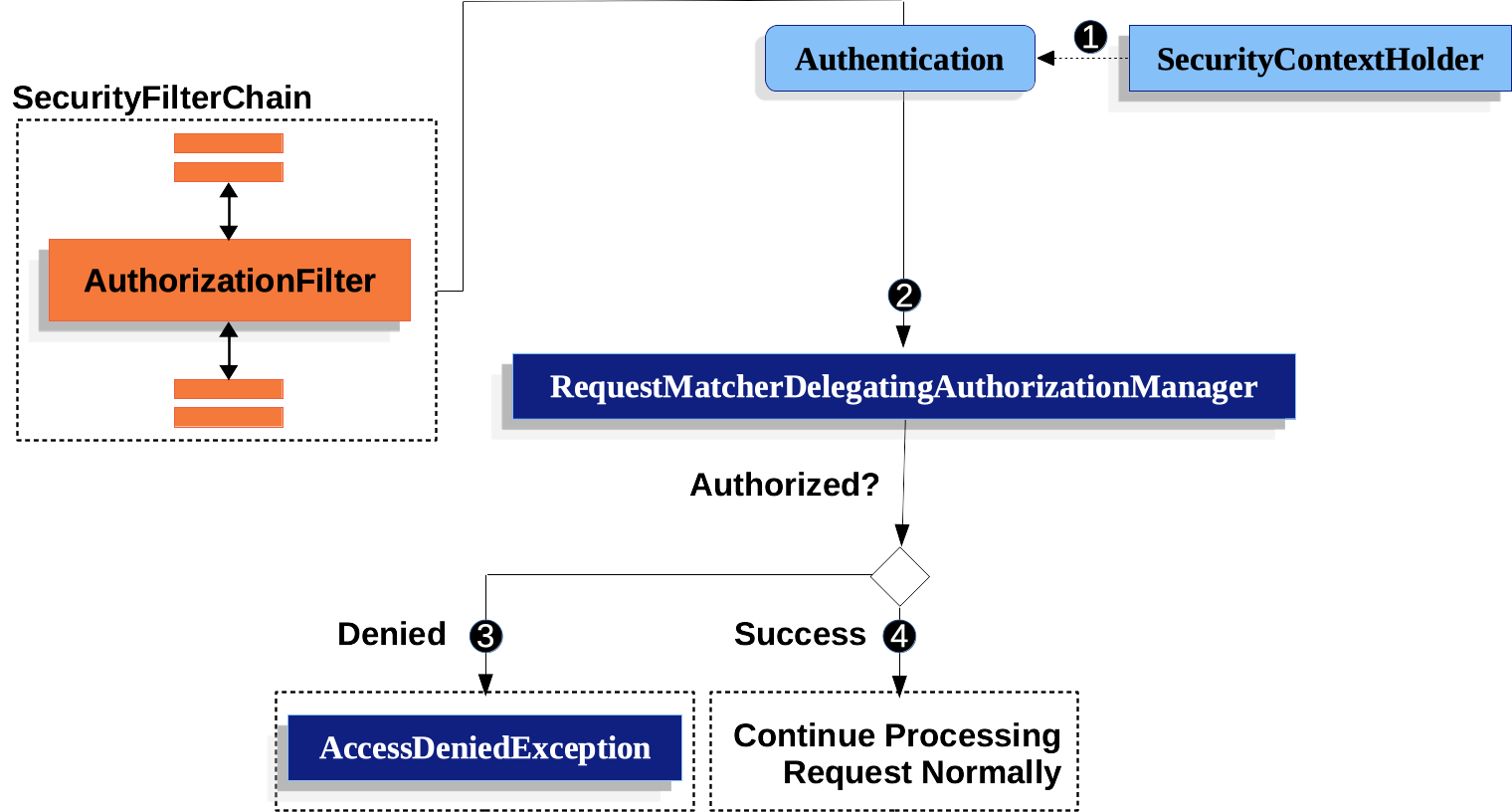
-
 首先,
首先,AuthorizationFilter从SecurityContextHolder获取Authentication。 它将其包装在Supplier以延迟查找。 -
 其次,它将
其次,它将Supplier<Authentication>和HttpServletRequest到AuthorizationManager.-
 如果授权被拒绝,则
如果授权被拒绝,则AccessDeniedException被抛出。 在这种情况下,ExceptionTranslationFilter处理AccessDeniedException. -
 如果授予访问权限,
如果授予访问权限,AuthorizationFilter继续使用 FilterChain,它允许应用程序正常处理。
-
我们可以通过按优先顺序添加更多规则来将 Spring Security 配置为具有不同的规则。
-
Java
@Bean
SecurityFilterChain web(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
// ...
.authorizeHttpRequests(authorize -> authorize (1)
.requestMatchers("/resources/**", "/signup", "/about").permitAll() (2)
.requestMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN") (3)
.requestMatchers("/db/**").access(new WebExpressionAuthorizationManager("hasRole('ADMIN') and hasRole('DBA')")) (4)
// .requestMatchers("/db/**").access(AuthorizationManagers.allOf(AuthorityAuthorizationManager.hasRole("ADMIN"), AuthorityAuthorizationManager.hasRole("DBA"))) (5)
.anyRequest().denyAll() (6)
);
return http.build();
}| 1 | 指定了多个授权规则。 每个规则都按照其声明的顺序进行考虑。 |
| 2 | 我们指定了任何用户都可以访问的多个 URL 模式。 具体而言,如果 URL 以“/resources/”开头、等于“/signup”或等于“/about”,则任何用户都可以访问请求。 |
| 3 | 任何以 “/admin/” 开头的 URL 都将被限制为具有 “ROLE_ADMIN” 角色的用户。
您会注意到,由于我们正在调用hasRole方法,则不需要指定 “ROLE_” 前缀。 |
| 4 | 任何以 “/db/” 开头的 URL 都要求用户同时具有 “ROLE_ADMIN” 和 “ROLE_DBA”。
您会注意到,由于我们使用的是hasRole表达式,则不需要指定 “ROLE_” 前缀。 |
| 5 | 4 中的相同规则,可以通过组合多个来编写AuthorizationManager. |
| 6 | 任何尚未匹配的 URL 都将被拒绝访问。 如果您不想意外忘记更新授权规则,这是一个很好的策略。 |
您可以通过构建自己的方法来采用基于 bean 的方法RequestMatcherDelegatingAuthorizationManager这样:
-
Java
@Bean
SecurityFilterChain web(HttpSecurity http, AuthorizationManager<RequestAuthorizationContext> access)
throws AuthenticationException {
http
.authorizeHttpRequests((authorize) -> authorize
.anyRequest().access(access)
)
// ...
return http.build();
}
@Bean
AuthorizationManager<RequestAuthorizationContext> requestMatcherAuthorizationManager(HandlerMappingIntrospector introspector) {
MvcRequestMatcher.Builder mvcMatcherBuilder = new MvcRequestMatcher.Builder(introspector);
RequestMatcher permitAll =
new AndRequestMatcher(
mvcMatcherBuilder.pattern("/resources/**"),
mvcMatcherBuilder.pattern("/signup"),
mvcMatcherBuilder.pattern("/about"));
RequestMatcher admin = mvcMatcherBuilder.pattern("/admin/**");
RequestMatcher db = mvcMatcherBuilder.pattern("/db/**");
RequestMatcher any = AnyRequestMatcher.INSTANCE;
AuthorizationManager<HttpServletRequest> manager = RequestMatcherDelegatingAuthorizationManager.builder()
.add(permitAll, (context) -> new AuthorizationDecision(true))
.add(admin, AuthorityAuthorizationManager.hasRole("ADMIN"))
.add(db, AuthorityAuthorizationManager.hasRole("DBA"))
.add(any, new AuthenticatedAuthorizationManager())
.build();
return (context) -> manager.check(context.getRequest());
}您还可以为任何请求匹配器连接自己的自定义授权管理器。
-
Java
@Bean
SecurityFilterChain web(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeHttpRequests((authorize) -> authorize
.requestMatchers("/my/authorized/endpoint").access(new CustomAuthorizationManager());
)
// ...
return http.build();
}或者你可以为所有请求提供它,如下所示:
-
Java
@Bean
SecurityFilterChain web(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeHttpRequests((authorize) -> authorize
.anyRequest().access(new CustomAuthorizationManager());
)
// ...
return http.build();
}默认情况下,AuthorizationFilter不适用于DispatcherType.ERROR和DispatcherType.ASYNC.
我们可以配置 Spring Security,以使用shouldFilterAllDispatcherTypes方法:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Bean
SecurityFilterChain web(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeHttpRequests((authorize) -> authorize
.shouldFilterAllDispatcherTypes(true)
.anyRequest.authenticated()
)
// ...
return http.build();
}@Bean
open fun web(http: HttpSecurity): SecurityFilterChain {
http {
authorizeHttpRequests {
shouldFilterAllDispatcherTypes = true
authorize(anyRequest, authenticated)
}
}
return http.build()
}现在,随着授权规则应用于所有 Dispatcher 类型,您可以更好地控制对它们的授权。
例如,您可能希望配置shouldFilterAllDispatcherTypes自true但不对 Dispatcher 类型的请求应用授权ASYNC或FORWARD.
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Bean
SecurityFilterChain web(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeHttpRequests((authorize) -> authorize
.shouldFilterAllDispatcherTypes(true)
.dispatcherTypeMatchers(DispatcherType.ASYNC, DispatcherType.FORWARD).permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
)
// ...
return http.build();
}@Bean
open fun web(http: HttpSecurity): SecurityFilterChain {
http {
authorizeHttpRequests {
shouldFilterAllDispatcherTypes = true
authorize(DispatcherTypeRequestMatcher(DispatcherType.ASYNC, DispatcherType.FORWARD), permitAll)
authorize(anyRequest, authenticated)
}
}
return http.build()
}您还可以对其进行自定义,以要求调度程序类型的特定角色:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Bean
SecurityFilterChain web(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeHttpRequests((authorize) -> authorize
.shouldFilterAllDispatcherTypes(true)
.dispatcherTypeMatchers(DispatcherType.ERROR).hasRole("ADMIN")
.anyRequest().authenticated()
)
// ...
return http.build();
}@Bean
open fun web(http: HttpSecurity): SecurityFilterChain {
http {
authorizeHttpRequests {
shouldFilterAllDispatcherTypes = true
authorize(DispatcherTypeRequestMatcher(DispatcherType.ERROR), hasRole("ADMIN"))
authorize(anyRequest, authenticated)
}
}
return http.build()
}请求匹配器
这RequestMatcherinterface 用于确定请求是否与给定规则匹配。
我们使用securityMatchers来确定给定的HttpSecurity应应用于给定请求。
同样,我们可以使用requestMatchers来确定我们应该应用于给定请求的授权规则。
请看下面的例子:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig {
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.securityMatcher("/api/**") (1)
.authorizeHttpRequests(authorize -> authorize
.requestMatchers("/user/**").hasRole("USER") (2)
.requestMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN") (3)
.anyRequest().authenticated() (4)
)
.formLogin(withDefaults());
return http.build();
}
}@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
open class SecurityConfig {
@Bean
open fun web(http: HttpSecurity): SecurityFilterChain {
http {
securityMatcher("/api/**") (1)
authorizeHttpRequests {
authorize("/user/**", hasRole("USER")) (2)
authorize("/admin/**", hasRole("ADMIN")) (3)
authorize(anyRequest, authenticated) (4)
}
}
return http.build()
}
}| 1 | 配置HttpSecurity仅应用于以/api/ |
| 2 | 允许访问以/user/对于具有USER角色 |
| 3 | 允许访问以/admin/对于具有ADMIN角色 |
| 4 | 与上述规则不匹配的任何其他请求都需要身份验证 |
这securityMatcher(s)和requestMatcher(s)方法将决定哪些RequestMatcherimplementation 最适合您的应用程序:如果 Spring MVC 在 Classpath 中,则MvcRequestMatcher,否则,AntPathRequestMatcher将被使用。
您可以在此处阅读有关 Spring MVC 集成的更多信息。
如果您想使用特定的RequestMatcher,只需将实现传递给securityMatcher和/或requestMatcher方法:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
import static org.springframework.security.web.util.matcher.AntPathRequestMatcher.antMatcher; (1)
import static org.springframework.security.web.util.matcher.RegexRequestMatcher.regexMatcher;
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig {
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.securityMatcher(antMatcher("/api/**")) (2)
.authorizeHttpRequests(authorize -> authorize
.requestMatchers(antMatcher("/user/**")).hasRole("USER") (3)
.requestMatchers(regexMatcher("/admin/.*")).hasRole("ADMIN") (4)
.requestMatchers(new MyCustomRequestMatcher()).hasRole("SUPERVISOR") (5)
.anyRequest().authenticated()
)
.formLogin(withDefaults());
return http.build();
}
}
public class MyCustomRequestMatcher implements RequestMatcher {
@Override
public boolean matches(HttpServletRequest request) {
// ...
}
}
import org.springframework.security.web.util.matcher.AntPathRequestMatcher.antMatcher (1)
import org.springframework.security.web.util.matcher.RegexRequestMatcher.regexMatcher
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
open class SecurityConfig {
@Bean
open fun web(http: HttpSecurity): SecurityFilterChain {
http {
securityMatcher(antMatcher("/api/**")) (2)
authorizeHttpRequests {
authorize(antMatcher("/user/**"), hasRole("USER")) (3)
authorize(regexMatcher("/admin/**"), hasRole("ADMIN")) (4)
authorize(MyCustomRequestMatcher(), hasRole("SUPERVISOR")) (5)
authorize(anyRequest, authenticated)
}
}
return http.build()
}
}
1
Import the static factory methods from AntPathRequestMatcher and RegexRequestMatcher to create RequestMatcher instances.
2
Configure HttpSecurity to only be applied to URLs that start with /api/, using AntPathRequestMatcher
3
Allow access to URLs that start with /user/ to users with the USER role, using AntPathRequestMatcher
4
Allow access to URLs that start with /admin/ to users with the ADMIN role, using RegexRequestMatcher
5
Allow access to URLs that match the MyCustomRequestMatcher to users with the SUPERVISOR role, using a custom RequestMatcher
Expressions
It is recommended that you use type-safe authorization managers instead of SpEL.
However, WebExpressionAuthorizationManager is available to help migrate legacy SpEL.
To use WebExpressionAuthorizationManager, you can construct one with the expression you are trying to migrate, like so:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
.requestMatchers("/test/**").access(new WebExpressionAuthorizationManager("hasRole('ADMIN') && hasRole('USER')"))
.requestMatchers("/test/**").access(WebExpressionAuthorizationManager("hasRole('ADMIN') && hasRole('USER')"))
If you are referring to a bean in your expression like so: @webSecurity.check(authentication, request), it’s recommended that you instead call the bean directly, which will look something like the following:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
.requestMatchers("/test/**").access((authentication, context) ->
new AuthorizationDecision(webSecurity.check(authentication.get(), context.getRequest())))
.requestMatchers("/test/**").access((authentication, context): AuthorizationManager<RequestAuthorizationContext> ->
AuthorizationDecision(webSecurity.check(authentication.get(), context.getRequest())))
For complex instructions that include bean references as well as other expressions, it is recommended that you change those to implement AuthorizationManager and refer to them by calling .access(AuthorizationManager).
If you are not able to do that, you can configure a DefaultHttpSecurityExpressionHandler with a bean resolver and supply that to WebExpressionAuthorizationManager#setExpressionhandler.