AMQP 支持
AMQP(RabbitMQ)支持
Spring Integration通过使用高级消息排队协议(AMQP)提供通道适配器用于接收和发送消息。
你需要把这种依赖性纳入你的项目中:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.integration</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-integration-amqp</artifactId>
<version>6.1.9</version>
</dependency>compile "org.springframework.integration:spring-integration-amqp:6.1.9"
以下适配器可供选择:
Spring 集成还提供点对点消息通道和由AMQP交换和队列支持的发布-订阅消息通道。
为了提供AMQP支持,Spring Integration依赖于(Spring AMQP),该平台将Spring核心概念应用于基于AMQP的消息解决方案开发。 Spring AMQP 提供了与 (Spring JMS) 类似的语义。
提供的AMQP通道适配器仅用于单向消息传输(发送或接收),而Spring Integration还提供用于请求-回复作的入站和出站AMQP网关。
提示: 你应该熟悉Spring AMQP项目的参考文档。 它提供了关于 Spring 与 AMQP 整体集成,特别是 RabbitMQ 的更深入信息。
入站通道适配器
以下列表展示了AMQP入站信道适配器的可能配置选项:
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow amqpInbound(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
return IntegrationFlow.from(Amqp.inboundAdapter(connectionFactory, "aName"))
.handle(m -> System.out.println(m.getPayload()))
.get();
}
@Bean
public MessageChannel amqpInputChannel() {
return new DirectChannel();
}
@Bean
public AmqpInboundChannelAdapter inbound(SimpleMessageListenerContainer listenerContainer,
@Qualifier("amqpInputChannel") MessageChannel channel) {
AmqpInboundChannelAdapter adapter = new AmqpInboundChannelAdapter(listenerContainer);
adapter.setOutputChannel(channel);
return adapter;
}
@Bean
public SimpleMessageListenerContainer container(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
SimpleMessageListenerContainer container =
new SimpleMessageListenerContainer(connectionFactory);
container.setQueueNames("aName");
container.setConcurrentConsumers(2);
// ...
return container;
}
@Bean
@ServiceActivator(inputChannel = "amqpInputChannel")
public MessageHandler handler() {
return new MessageHandler() {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message<?> message) throws MessagingException {
System.out.println(message.getPayload());
}
};
}
<int-amqp:inbound-channel-adapter
id="inboundAmqp" (1)
channel="inboundChannel" (2)
queue-names="si.test.queue" (3)
acknowledge-mode="AUTO" (4)
advice-chain="" (5)
channel-transacted="" (6)
concurrent-consumers="" (7)
connection-factory="" (8)
error-channel="" (9)
expose-listener-channel="" (10)
header-mapper="" (11)
mapped-request-headers="" (12)
listener-container="" (13)
message-converter="" (14)
message-properties-converter="" (15)
phase="" (16)
prefetch-count="" (17)
receive-timeout="" (18)
recovery-interval="" (19)
missing-queues-fatal="" (20)
shutdown-timeout="" (21)
task-executor="" (22)
transaction-attribute="" (23)
transaction-manager="" (24)
tx-size="" (25)
consumers-per-queue (26)
batch-mode="MESSAGES"/> (27)
<1> The unique ID for this adapter.
Optional.
<2> Message channel to which converted messages should be sent.
Required.
<3> Names of the AMQP queues (comma-separated list) from which messages should be consumed.
Required.
<4> Acknowledge mode for the `MessageListenerContainer`.
When set to `MANUAL`, the delivery tag and channel are provided in message headers `amqp_deliveryTag` and `amqp_channel`, respectively.
The user application is responsible for acknowledgement.
`NONE` means no acknowledgements (`autoAck`).
`AUTO` means the adapter's container acknowledges when the downstream flow completes.
Optional (defaults to AUTO).
See <<amqp-inbound-ack>>.
<5> Extra AOP Advices to handle cross-cutting behavior associated with this inbound channel adapter.
Optional.
<6> Flag to indicate that channels created by this component are transactional.
If true, it tells the framework to use a transactional channel and to end all operations (send or receive) with a commit or rollback, depending on the outcome, with an exception that signals a rollback.
Optional (Defaults to false).
<7> Specify the number of concurrent consumers to create.
The default is `1`.
We recommend raising the number of concurrent consumers to scale the consumption of messages coming in from a queue.
However, note that any ordering guarantees are lost once multiple consumers are registered.
In general, use one consumer for low-volume queues.
Not allowed when 'consumers-per-queue' is set.
Optional.
<8> Bean reference to the RabbitMQ `ConnectionFactory`.
Optional (defaults to `connectionFactory`).
<9> Message channel to which error messages should be sent.
Optional.
<10> Whether the listener channel (com.rabbitmq.client.Channel) is exposed to a registered `ChannelAwareMessageListener`.
Optional (defaults to true).
<11> A reference to an `AmqpHeaderMapper` to use when receiving AMQP Messages.
Optional.
By default, only standard AMQP properties (such as `contentType`) are copied to Spring Integration `MessageHeaders`.
Any user-defined headers within the AMQP `MessageProperties` are NOT copied to the message by the default `DefaultAmqpHeaderMapper`.
Not allowed if 'request-header-names' is provided.
<12> Comma-separated list of the names of AMQP Headers to be mapped from the AMQP request into the `MessageHeaders`.
This can only be provided if the 'header-mapper' reference is not provided.
The values in this list can also be simple patterns to be matched against the header names (such as "\*" or "thing1*, thing2" or "*something").
<13> Reference to the `AbstractMessageListenerContainer` to use for receiving AMQP Messages.
If this attribute is provided, no other attribute related to the listener container configuration should be provided.
In other words, by setting this reference, you must take full responsibility for the listener container configuration.
The only exception is the `MessageListener` itself.
Since that is actually the core responsibility of this channel adapter implementation, the referenced listener container must not already have its own `MessageListener`.
Optional.
<14> The `MessageConverter` to use when receiving AMQP messages.
Optional.
<15> The `MessagePropertiesConverter` to use when receiving AMQP messages.
Optional.
<16> Specifies the phase in which the underlying `AbstractMessageListenerContainer` should be started and stopped.
The startup order proceeds from lowest to highest, and the shutdown order is the reverse of that.
By default, this value is `Integer.MAX_VALUE`, meaning that this container starts as late as possible and stops as soon as possible.
Optional.
<17> Tells the AMQP broker how many messages to send to each consumer in a single request.
Often, you can set this value high to improve throughput.
It should be greater than or equal to the transaction size (see the `tx-size` attribute, later in this list).
Optional (defaults to `1`).
<18> Receive timeout in milliseconds.
Optional (defaults to `1000`).
<19> Specifies the interval between recovery attempts of the underlying `AbstractMessageListenerContainer` (in milliseconds).
Optional (defaults to `5000`).
<20> If 'true' and none of the queues are available on the broker, the container throws a fatal exception during startup and stops if the queues are deleted when the container is running (after making three attempts to passively declare the queues).
If `false`, the container does not throw an exception and goes into recovery mode, attempting to restart according to the `recovery-interval`.
Optional (defaults to `true`).
<21> The time to wait for workers (in milliseconds) after the underlying `AbstractMessageListenerContainer` is stopped and before the AMQP connection is forced closed.
If any workers are active when the shutdown signal comes, they are allowed to finish processing as long as they can finish within this timeout.
Otherwise, the connection is closed and messages remain unacknowledged (if the channel is transactional).
Optional (defaults to `5000`).
<22> By default, the underlying `AbstractMessageListenerContainer` uses a `SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor` implementation, that fires up a new thread for each task, running it asynchronously.
By default, the number of concurrent threads is unlimited.
Note that this implementation does not reuse threads.
Consider using a thread-pooling `TaskExecutor` implementation as an alternative.
Optional (defaults to `SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor`).
<23> By default, the underlying `AbstractMessageListenerContainer` creates a new instance of the `DefaultTransactionAttribute` (it takes the EJB approach to rolling back on runtime but not checked exceptions).
Optional (defaults to `DefaultTransactionAttribute`).
<24> Sets a bean reference to an external `PlatformTransactionManager` on the underlying `AbstractMessageListenerContainer`.
The transaction manager works in conjunction with the `channel-transacted` attribute.
If there is already a transaction in progress when the framework is sending or receiving a message and the `channelTransacted` flag is `true`, the commit or rollback of the messaging transaction is deferred until the end of the current transaction.
If the `channelTransacted` flag is `false`, no transaction semantics apply to the messaging operation (it is auto-acked).
For further information, see
https://docs.spring.io/spring-amqp/reference/html/%255Freference.html#%5Ftransactions[Transactions with Spring AMQP].
Optional.
<25> Tells the `SimpleMessageListenerContainer` how many messages to process in a single transaction (if the channel is transactional).
For best results, it should be less than or equal to the value set in `prefetch-count`.
Not allowed when 'consumers-per-queue' is set.
Optional (defaults to `1`).
<26> Indicates that the underlying listener container should be a `DirectMessageListenerContainer` instead of the default `SimpleMessageListenerContainer`.
See the https://docs.spring.io/spring-amqp/reference/html/[Spring AMQP Reference Manual] for more information.
<27> When the container's `consumerBatchEnabled` is `true`, determines how the adapter presents the batch of messages in the message payload.
When set to `MESSAGES` (default), the payload is a `List<Message<?>>` where each message has headers mapped from the incoming AMQP `Message` and the payload is the converted `body`.
When set to `EXTRACT_PAYLOADS`, the payload is a `List<?>` where the elements are converted from the AMQP `Message` body.
`EXTRACT_PAYLOADS_WITH_HEADERS` is similar to `EXTRACT_PAYLOADS` but, in addition, the headers from each message are mapped from the `MessageProperties` into a `List<Map<String, Object>` at the corresponding index; the header name is `AmqpInboundChannelAdapter.CONSOLIDATED_HEADERS`.|
容器
注意,在配置带有XML的外部容器时,不能使用Spring AMQP命名空间来定义容器。
这是因为命名空间至少需要一个 |
尽管春季集成JMS和AMQP的支持相似,但存在重要差异。
JMS入站通道适配器使用的是Jms目的地民调来源在被子里,期待一个配置好的轮询器。
AMQP入站通道适配器使用以下摘要MessageListenerContainer并且以信息驱动。
在这方面,它更类似于JMS的消息驱动通道适配器。 |
从5.5版本开始,Amqp入站通道适配器可以配置为org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.retry.MessageRecoverer该策略用于恢复回调当重试作在内部被调用时。
看setMessageRecoveryer()更多信息请参见JavaDocs。
这@Publisher注释也可以与@RabbitListener:
@Configuration
@EnableIntegration
@EnableRabbit
@EnablePublisher
public static class ContextConfiguration {
@Bean
QueueChannel fromRabbitViaPublisher() {
return new QueueChannel();
}
@RabbitListener(queuesToDeclare = @Queue("publisherQueue"))
@Publisher("fromRabbitViaPublisher")
@Payload("#args.payload.toUpperCase()")
public void consumeForPublisher(String payload) {
}
}
默认情况下,@PublisherAOP 拦截器处理方法调用的返回值。
然而,来自@RabbitListener方法被视为AMQP回复消息。
因此,这种方法不能与@Publisher,所以@Payload推荐将相应的SpEL表达式与方法参数进行注释。
查看更多关于@Publisher在注释驱动配置部分。
在监听器容器中使用独占或单主动消费者时,建议设置容器属性强制停止自true.
这样可以防止在停止容器后,其他消费者在该实例完全停止前开始接收消息的情况。 |
批量消息
有关批量消息的更多信息,请参阅春季AMQP文档。
要用 Spring Integration 生成批量消息,只需配置出站端点批量处理兔子模板.
在接收批量消息时,默认情况下,监听器容器会提取每个片段消息,适配器会生成留言<?>对每个碎片。
从5.2版本开始,如果容器是deBatchingEnabled属性设置为false,去批处理由适配器执行,且消息<列表<?>>以 作为片段有效载荷列表(如适当转换而成)。
默认批次处理策略是简单批处理策略但适配器可以覆盖此设置。
这org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.retry.MessageBatchRecoverer当需要恢复进行重试作时,必须与批次一起使用。 |
轮询入信道适配器
概述
5.0.1版本引入了轮询通道适配器,允许你按需获取单个消息——例如,使用消息来源投票模板或者投票员。
更多信息请参见延迟确认可投票消息源。
目前它不支持 XML 配置。
以下示例展示了如何配置Amqp消息源:
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow flow() {
return IntegrationFlow.from(Amqp.inboundPolledAdapter(connectionFactory(), DSL_QUEUE),
e -> e.poller(Pollers.fixedDelay(1_000)).autoStartup(false))
.handle(p -> {
...
})
.get();
}
@Bean
public AmqpMessageSource source(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
return new AmqpMessageSource(connectionFactory, "someQueue");
}
关于配置属性,请参见 Javadoc。
This adapter currently does not have XML configuration support.入站网关
入站网关支持入站信道适配器上的所有属性(除了“通道”被“请求通道”替换),以及一些额外的属性。 以下列表展示了可用的属性:
@Bean // return the upper cased payload
public IntegrationFlow amqpInboundGateway(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
return IntegrationFlow.from(Amqp.inboundGateway(connectionFactory, "foo"))
.transform(String.class, String::toUpperCase)
.get();
}
@Bean
public MessageChannel amqpInputChannel() {
return new DirectChannel();
}
@Bean
public AmqpInboundGateway inbound(SimpleMessageListenerContainer listenerContainer,
@Qualifier("amqpInputChannel") MessageChannel channel) {
AmqpInboundGateway gateway = new AmqpInboundGateway(listenerContainer);
gateway.setRequestChannel(channel);
gateway.setDefaultReplyTo("bar");
return gateway;
}
@Bean
public SimpleMessageListenerContainer container(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
SimpleMessageListenerContainer container =
new SimpleMessageListenerContainer(connectionFactory);
container.setQueueNames("foo");
container.setConcurrentConsumers(2);
// ...
return container;
}
@Bean
@ServiceActivator(inputChannel = "amqpInputChannel")
public MessageHandler handler() {
return new AbstractReplyProducingMessageHandler() {
@Override
protected Object handleRequestMessage(Message<?> requestMessage) {
return "reply to " + requestMessage.getPayload();
}
};
}
<int-amqp:inbound-gateway
id="inboundGateway" (1)
request-channel="myRequestChannel" (2)
header-mapper="" (3)
mapped-request-headers="" (4)
mapped-reply-headers="" (5)
reply-channel="myReplyChannel" (6)
reply-timeout="1000" (7)
amqp-template="" (8)
default-reply-to="" /> (9)| 1 | 该适配器的唯一ID。 自选。 |
| 2 | 消息通道,转换为后消息发送到该通道。 必填。 |
| 3 | 对AmqpHeaderMapper用于接收AMQP消息。
自选。
默认情况下,只有标准AMQP属性(例如:内容类型)被复制到Spring Integration之间消息头.
AMQP 内任何用户自定义的头部消息属性默认情况下,不会复制到或复制 AMQP 消息DefaultAmqpHeaderMapper.
如果提供了“request-header-names”或“reply-header-names”,则不允许。 |
| 4 | AMQP头部名称的逗号分隔列表,从AMQP请求映射到以下消息头.
只有在未提供“头部映射器”引用时,才能提供该属性。
该列表中的值也可以是简单的模式,用于与头部名称匹配(例如: 或"*"“东西1*,东西2”或“*东西1”). |
| 5 | 逗号分隔的姓名列表消息头映射到AMQP回复消息的AMQP消息属性中。
所有标准头部(例如内容类型)映射到AMQP消息属性,而用户自定义的头映射到“头”属性。
只有在未提供“头部映射器”引用时,才能提供该属性。
该列表中的值也可以是简单的模式,用于与头部名称匹配(例如,或"*"“福*,酒吧”或“*福”). |
| 6 | 消息通道,期望回复消息。 自选。 |
| 7 | 设收到超时关于标的o.s.i.core.消息模板用于接收来自回复频道的消息。
如果未指定,该性质默认为1000(1秒)
只有当容器线程在回复发送前交接给另一个线程时才适用。 |
| 8 | 定制化Amqp模板BEAN 引用(以便更好地控制回复消息的发送)。
你可以提供另一种实现兔子模板. |
| 9 | 这回复 o.s.amqp.core.地址当请求消息没有回复财产。
如果没有指定这个选项,则不行AMQP-模板提供时,不回复请求消息中存在属性,且
一非法州例外是因为回复无法路由而被抛出。
如果未指定该选项且外部AMQP-模板提供例外,不予提出例外。
你必须选择这个选项,或者配置默认设置交换和路由键基于那个模板,
如果你预期情况不行回复请求消息中存在属性。 |
请参见入站信道适配器中关于配置监听器容器属性。
从5.5版本开始,Amqp入站通道适配器可以配置为org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.retry.MessageRecoverer该策略用于恢复回调当重试作在内部被调用时。
看setMessageRecoveryer()更多信息请参见JavaDocs。
批量消息
参见批量消息。
入站端点确认模式
默认情况下,入站端点使用自动确认模式,意味着当下游集成流程完成时,容器会自动确认消息(或通过使用队列通道或执行者频道).
将模式设置为没有配置消费者,使得完全不使用确认(代理在消息发送后自动确认)。
将模式设置为手动允许用户代码在处理过程中的其他时刻确认消息。
为此,在该模式中,端点提供渠道和配送标签在amqp_channel和amqp_deliveryTag分别是标题。
你可以对渠道但通常,只有基本的和basicNack(或basicReject)被使用。
为了不干扰容器的作,你不应保留对通道的引用,只应在当前消息的上下文中使用。
自从......渠道是对“活”对象的引用,无法序列化,且如果消息被持久化则丢失。 |
以下示例展示了你可以如何使用手动确认:
@ServiceActivator(inputChannel = "foo", outputChannel = "bar")
public Object handle(@Payload String payload, @Header(AmqpHeaders.CHANNEL) Channel channel,
@Header(AmqpHeaders.DELIVERY_TAG) Long deliveryTag) throws Exception {
// Do some processing
if (allOK) {
channel.basicAck(deliveryTag, false);
// perhaps do some more processing
}
else {
channel.basicNack(deliveryTag, false, true);
}
return someResultForDownStreamProcessing;
}
出站端点
以下出站端点有许多类似的配置选项。
从5.2版本开始,确认超时已被添加。
通常,当发布者确认启用时,经纪人会迅速返回一个确认(ack)或 nack,并将其发送到相应的渠道。
如果在收到确认前通道被关闭,Spring AMQP框架将合成一个nack。
“缺失”确认码本不应该发生,但如果你设置了这个属性,端点会定期检查确认,并在时间过后未收到确认时合成一个 nack。
出站通道适配器
以下示例展示了AMQP出站信道适配器可用的特性:
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow amqpOutbound(AmqpTemplate amqpTemplate,
MessageChannel amqpOutboundChannel) {
return IntegrationFlow.from(amqpOutboundChannel)
.handle(Amqp.outboundAdapter(amqpTemplate)
.routingKey("queue1")) // default exchange - route to queue 'queue1'
.get();
}
@Bean
@ServiceActivator(inputChannel = "amqpOutboundChannel")
public AmqpOutboundEndpoint amqpOutbound(AmqpTemplate amqpTemplate) {
AmqpOutboundEndpoint outbound = new AmqpOutboundEndpoint(amqpTemplate);
outbound.setRoutingKey("queue1"); // default exchange - route to queue 'queue1'
return outbound;
}
@Bean
public MessageChannel amqpOutboundChannel() {
return new DirectChannel();
}
<int-amqp:outbound-channel-adapter id="outboundAmqp" (1)
channel="outboundChannel" (2)
amqp-template="myAmqpTemplate" (3)
exchange-name="" (4)
exchange-name-expression="" (5)
order="1" (6)
routing-key="" (7)
routing-key-expression="" (8)
default-delivery-mode"" (9)
confirm-correlation-expression="" (10)
confirm-ack-channel="" (11)
confirm-nack-channel="" (12)
confirm-timeout="" (13)
wait-for-confirm="" (14)
return-channel="" (15)
error-message-strategy="" (16)
header-mapper="" (17)
mapped-request-headers="" (18)
lazy-connect="true" (19)
multi-send="false"/> (20)| 1 | 该适配器的唯一ID。 自选。 |
| 2 | 消息通道,消息应发送至该通道以便转换为并发布到AMQP交换机。 必填。 |
| 3 | Bean 对已配置的 AMQP 模板的引用。可选(默认为amqp模板). |
| 4 | 发送消息的AMQP交换机名称。 如果未提供,消息会发送到默认的无名交换机。 与“交换名-表达式”互斥。 自选。 |
| 5 | 一个 SpEL 表达式,用于计算消息发送至 AMQP 交换的名称,消息作为根对象。如果未提供,消息发送到默认的无名称交换。与“交换名”互斥。 自选。 |
| 6 | 当多个消费者注册时,该消费者的顺序,从而实现负载均衡和故障转移。可选(默认为Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE [=Integer.MAX_VALUE]). |
| 7 | 发送消息时使用的固定路由密钥。
默认情况下,这是一个空的字符串. 与“路由密钥表达式”互斥。 自选。 |
| 8 | 一个 SpEL 表达式,用于计算发送消息时使用的路由键,消息作为根对象(例如 'payload.key')。
默认情况下,这是一个空的字符串. 与“路由密钥”互斥。 自选。 |
| 9 | 消息的默认传递方式:持续或NON_PERSISTENT. 如果头部映射器设定送达方式。
如果 Spring Integration 消息头amqp_deliveryMode存在,DefaultHeaderMapper设置该值。如果未提供该属性且头部映射器未设置,默认值依赖于底层的Spring AMQPMessageProperties转换器被以下机构使用兔子模板.
如果完全没有自定义,默认是持续. 自选。 |
| 10 | 定义相关数据的表达式。提供后,配置底层AMQP模板以接收发布者确认。需要专用兔子模板以及一个缓存连接工厂其中出版社确认属性设置为true. 当收到发布者确认并提供相关数据时,会写入确认-确认-通道或者确认-nack-频道,取决于确认类型。确认的有效载荷是相关数据,定义如下表达式。消息的“amqp_publishConfirm”头设置为true (啊)或false (纳克). 例子:头部['myCorrelationData']和有效载荷. 4.1 版本引入了amqp_publishConfirmNackCause消息头。它包含原因对发布商确认的“nack”表示。从4.2版本开始,如果表达式解析为留言<?>实例(例如#this),在啊/纳克通道基于该消息,并添加额外的头部。此前,新消息的有效载荷是基于相关数据,无论类型如何。另见发布者确认和返回的替代机制。 自选。 |
| 11 | 正向的通道(啊) 发布者确认已发送。有效载荷是由确认-相关-表达.
如果表达式为#root或#this,消息由原始消息构建,其中amqp_publishConfirm头部设置为true. 另见“发布者确认和返回的替代机制”。可选(默认为零通道). |
| 12 | 负向的通道(纳克) 发送发布者确认。有效载荷是由确认-相关-表达(如果没有错误消息策略已配置)。
如果表达式为#root或#this,消息由原始消息构建,其中amqp_publishConfirm头部设置为false.
当有错误消息策略,消息是错误消息其中NackedAmqpMessageException有效载荷。
另见出版商确认与退货的替代机制。
可选(默认为零通道). |
| 13 | 设置后,如果发布者确认未在毫秒级内收到,适配器会合成负向确认(nack)。待处理确认每50%检查一次,因此nack实际发送时间介于1倍到1.5倍之间。另见发布者确认和返回的替代机制。默认无(nacks不会生成)。 |
| 14 | 当设置为 true,调用线程会阻塞,等待发布者确认。这需要兔子模板配置为确认以及确认-相关-表达. 线程最多会被阻塞确认超时(或默认为5秒)。如果发生超时,一个MessageTimeoutException将被抛出。如果启用返回且返回消息,或在等待确认期间发生其他异常,则消息处理异常将被抛掷,并附上适当的信息。 |
| 15 | 返回消息发送到的信道。
当提供时,底层的AMQP模板被配置为返回不可投递的消息给适配器。
没有错误消息策略配置完成后,消息由AMQP接收到的数据构成,并附加以下额外头部:amqp_returnReplyCode,amqp_returnReplyText,amqp_returnExchange,amqp_returnRoutingKey.
当有错误消息策略,消息是错误消息其中返回AmqpMessageException有效载荷。
另见出版商确认与退货的替代机制。
自选。 |
| 16 | 对错误消息策略用于构建的实现错误消息发送回应或负面确认消息的情况。 |
| 17 | 对AmqpHeaderMapper用于发送AMQP消息。默认情况下,仅有标准AMQP属性(例如:内容类型)被复制到 Spring 集成中消息头. 默认的“DefaultAmqpHeaderMapper”不会将任何用户自定义的头部复制到消息中。如果提供了“request-header-names”,则不允许。 自选。 |
| 18 | 要映射的AMQP头部名称的逗号分隔列表消息头到AMQP消息。如果提供了“头部映射器”引用,则不允许。该列表中的值也可以是简单的模式,用于与头部名称匹配(例如: 或"*"“东西1*,东西2”或“*东西1”). |
| 19 | 当设置为false端点在应用上下文初始化时尝试连接到代理。这允许“快速失败”检测错误配置,但如果代理宕机,初始化也会失败。 什么时候true(默认)连接在发送第一条消息时建立(如果连接尚未存在,因为其他组件建立了连接)。 |
| 20 | 当设置为true,类型的有效载荷可迭代<消息吗<?>>将作为离散消息在同一信道内发送,且在单一范围内兔子模板调用。 需要兔子模板. 什么时候等待确认是真的,RabbitTemplate.waitForConfirmsOrDie()在消息发送后调用。使用事务模板时,发送会在新事务中执行,或在已启动的事务中执行(如果存在)。 |
|
回传通道
使用 |
出站网关
以下列表展示了AMQP出站网关可能的属性:
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow amqpOutbound(AmqpTemplate amqpTemplate) {
return f -> f.handle(Amqp.outboundGateway(amqpTemplate)
.routingKey("foo")) // default exchange - route to queue 'foo'
.get();
}
@MessagingGateway(defaultRequestChannel = "amqpOutbound.input")
public interface MyGateway {
String sendToRabbit(String data);
}
@Bean
@ServiceActivator(inputChannel = "amqpOutboundChannel")
public AmqpOutboundEndpoint amqpOutbound(AmqpTemplate amqpTemplate) {
AmqpOutboundEndpoint outbound = new AmqpOutboundEndpoint(amqpTemplate);
outbound.setExpectReply(true);
outbound.setRoutingKey("foo"); // default exchange - route to queue 'foo'
return outbound;
}
@Bean
public MessageChannel amqpOutboundChannel() {
return new DirectChannel();
}
@MessagingGateway(defaultRequestChannel = "amqpOutboundChannel")
public interface MyGateway {
String sendToRabbit(String data);
}
<int-amqp:outbound-gateway id="outboundGateway" (1)
request-channel="myRequestChannel" (2)
amqp-template="" (3)
exchange-name="" (4)
exchange-name-expression="" (5)
order="1" (6)
reply-channel="" (7)
reply-timeout="" (8)
requires-reply="" (9)
routing-key="" (10)
routing-key-expression="" (11)
default-delivery-mode"" (12)
confirm-correlation-expression="" (13)
confirm-ack-channel="" (14)
confirm-nack-channel="" (15)
confirm-timeout="" (16)
return-channel="" (17)
error-message-strategy="" (18)
lazy-connect="true" /> (19)| 1 | 该适配器的唯一ID。 自选。 |
| 2 | 消息通道,消息被发送至以进行转换并发布到AMQP交换机。 必填。 |
| 3 | Bean 对已配置的 AMQP 模板的引用。可选(默认为amqp模板). |
| 4 | 消息应发送到的AMQP交换地址名称。如果未提供,消息将发送到默认的无名称cxchange。与“exchange-name-expression”互斥。 自选。 |
| 5 | 一个 SpEL 表达式,用于评估消息应发送至 AMQP 交换的名称,消息作为根对象。如果未提供,消息将发送到默认的无名称交换。与“交换名”互斥。 自选。 |
| 6 | 当多个消费者注册时,该消费者的顺序,从而实现负载均衡和故障转移。可选(默认为Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE [=Integer.MAX_VALUE]). |
| 7 | 消息通道,回复应在收到AMQP队列并转换后发送。 自选。 |
| 8 | 网关在向回复信道. 这只适用于回复信道可以阻挡——例如队列通道目前容量上限已满。默认为无限。 |
| 9 | 什么时候true,如果在AmqpTemplate的“replyTimeout”财产。 默认true. |
| 10 | 这路由密钥用于发送消息。
默认情况下,这是一个空的字符串. 与“路由密钥表达式”互斥。 自选。 |
| 11 | 一个被评估以确定路由密钥用于发送消息时,以消息为根对象(例如,'payload.key')。
默认情况下,这是一个空的字符串. 与“路由密钥”互斥。 自选。 |
| 12 | 消息的默认传递方式:持续或NON_PERSISTENT. 如果头部映射器设定送达方式。
如果 Spring Integration 消息头amqp_deliveryMode存在,DefaultHeaderMapper设置该值。如果未提供该属性且头部映射器未设置,默认值依赖于底层的Spring AMQPMessageProperties转换器被以下机构使用兔子模板.
如果完全没有自定义,默认是持续. 自选。 |
| 13 | 自4.2版本起。
定义相关数据的表达式。
提供后,该模板会配置底层AMQP模板以接收发布者确认。
需要专用兔子模板以及一个缓存连接工厂其中出版社确认属性设置为true.
当收到发布确认并提供相关数据时,会写入确认-确认-通道或者确认-nack-频道,取决于确认类型。
确认的有效载荷是相关数据,定义如下。
该消息的头部“amqp_publishConfirm”设置为true (啊)或false (纳克). 为纳克确认,Spring Integration 提供了额外的头部amqp_publishConfirmNackCause.
例子:头部['myCorrelationData']和有效载荷. 如果表达式解析为留言<?>实例(例如#this),信息
在啊/纳克通道基于该消息,并添加了额外的头部。
此前,新消息的有效载荷是基于相关数据,无论类型如何。
另见出版商确认与退货的替代机制。
自选。 |
| 14 | 正向的通道(啊) 已发送出版商确认函件。
有效载荷是定义的相关性数据确认-相关-表达.
如果表达式为#root或#this,消息由原始消息构建,其中amqp_publishConfirm头部设置为true. 另见“发布者确认和返回的替代机制”。可选(默认为零通道). |
| 15 | 负向的通道(纳克) 已发送出版商确认函件。
有效载荷是定义的相关性数据确认-相关-表达(如果没有错误消息策略已配置)。
如果表达式为#root或#this,消息由原始消息构建,其中amqp_publishConfirm头部设置为false.
当有错误消息策略,消息是错误消息其中NackedAmqpMessageException有效载荷。
另见出版商确认与退货的替代机制。
可选(默认为零通道). |
| 16 | 设置后,如果发布者确认未在毫秒内收到,网关会合成负确认(nack)。 待确认每50%检查一次,因此实际发送nack的时间介于1倍到1.5倍之间。 默认为无(nacks不会生成)。 |
| 17 | 返回消息发送到的信道。
当提供时,底层的AMQP模板被配置为返回不可投递的消息给适配器。
没有错误消息策略配置完成后,消息由AMQP接收到的数据构成,并附加以下额外头部:amqp_returnReplyCode,amqp_returnReplyText,amqp_returnExchange和amqp_returnRoutingKey.
当有错误消息策略,消息是错误消息其中返回AmqpMessageException有效载荷。
另见出版商确认与退货的替代机制。
自选。 |
| 18 | 对错误消息策略用于构建的实现错误消息发送回应或负面确认消息的情况。 |
| 19 | 当设置为false,端点在应用上下文初始化期间尝试连接到代理。
这允许通过在代理程序宕机时记录错误消息,实现“快速故障”检测错误配置。
什么时候true(默认)连接在发送第一条消息时建立(如果连接尚未存在,因为其他组件建立了连接)。 |
|
回传通道
使用 |
基础Amqp模板有默认值回复Timeout五秒钟。
如果你需要更长的超时,必须在模板. |
注意,出站适配器和出站网关配置的唯一区别是设置期待回复财产。
异步出站网关
前一节讨论的网关是同步的,发送线程会被暂停,直到
回复已收到(或发生超时)。
Spring Integration 4.3 版本增加了异步网关,使用异步兔子模板来自春季AMQP。
发送消息后,线程在发送作完成后立即返回,收到消息后,回复会通过模板的监听器容器线程发送。
当网关在轮询线程中被调用时,这非常有用。
线程已发布,可用于框架内的其他任务。
以下列表展示了AMQP异步出站网关的可能配置选项:
@Configuration
public class AmqpAsyncApplication {
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow asyncAmqpOutbound(AsyncRabbitTemplate asyncRabbitTemplate) {
return f -> f
.handle(Amqp.asyncOutboundGateway(asyncRabbitTemplate)
.routingKey("queue1")); // default exchange - route to queue 'queue1'
}
@MessagingGateway(defaultRequestChannel = "asyncAmqpOutbound.input")
public interface MyGateway {
String sendToRabbit(String data);
}
}
@Configuration
public class AmqpAsyncConfig {
@Bean
@ServiceActivator(inputChannel = "amqpOutboundChannel")
public AsyncAmqpOutboundGateway amqpOutbound(AsyncRabbitTemplate asyncTemplate) {
AsyncAmqpOutboundGateway outbound = new AsyncAmqpOutboundGateway(asyncTemplate);
outbound.setRoutingKey("foo"); // default exchange - route to queue 'foo'
return outbound;
}
@Bean
public AsyncRabbitTemplate asyncTemplate(RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate,
SimpleMessageListenerContainer replyContainer) {
return new AsyncRabbitTemplate(rabbitTemplate, replyContainer);
}
@Bean
public SimpleMessageListenerContainer replyContainer() {
SimpleMessageListenerContainer container = new SimpleMessageListenerContainer(ccf);
container.setQueueNames("asyncRQ1");
return container;
}
@Bean
public MessageChannel amqpOutboundChannel() {
return new DirectChannel();
}
}
<int-amqp:outbound-async-gateway id="asyncOutboundGateway" (1)
request-channel="myRequestChannel" (2)
async-template="" (3)
exchange-name="" (4)
exchange-name-expression="" (5)
order="1" (6)
reply-channel="" (7)
reply-timeout="" (8)
requires-reply="" (9)
routing-key="" (10)
routing-key-expression="" (11)
default-delivery-mode"" (12)
confirm-correlation-expression="" (13)
confirm-ack-channel="" (14)
confirm-nack-channel="" (15)
confirm-timeout="" (16)
return-channel="" (17)
lazy-connect="true" /> (18)| 1 | 该适配器的唯一ID。 自选。 |
| 2 | 消息通道,消息应发送至该通道,以便转换为并发布到AMQP交换机。 必填。 |
| 3 | Bean 对配置的引用异步兔子模板. 可选(默认为async兔子模板). |
| 4 | 消息应发送到的AMQP交换名称。如果未提供,消息将发送到默认的无名称交换。与“交换名表达式”互斥。 自选。 |
| 5 | 一个 SpEL 表达式,用于计算消息发送至 AMQP 交换的名称,消息作为根对象。如果未提供,消息发送到默认的无名称交换。与“交换名”互斥。 自选。 |
| 6 | 当多个消费者注册时,该消费者的顺序,从而实现负载均衡和故障转移。可选(默认为Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE [=Integer.MAX_VALUE]). |
| 7 | 消息通道,回复应在收到AMQP队列并转换后发送。 自选。 |
| 8 | 网关在向回复信道. 这只适用于回复信道可以阻挡——例如队列通道目前容量上限已满。默认是无限。 |
| 9 | 当没有收到回复消息时,AsyncRabbitTemplate 的“receiveTimeout”属性,该设置为true网关向入站消息发送错误消息errorChannel页眉。 当没有收到回复消息时,AsyncRabbitTemplate 的“receiveTimeout”属性,该设置为false网关向默认发送错误消息errorChannel(如果有的话)。默认为true. |
| 10 | 发送消息时使用的路由密钥。默认情况下,这是空的字符串. 与“路由密钥表达式”互斥。 自选。 |
| 11 | 一个用于计算用于确定发送消息时使用的路由密钥的 SpEL 表达式,以消息为根对象(例如,'payload.key')。默认情况下,这是空的字符串. 与“路由密钥”互斥。 自选。 |
| 12 | 消息的默认传递方式:持续或NON_PERSISTENT. 如果头部映射器设置了传递模式。如果 Spring Integration 消息头(amqp_deliveryMode)存在,则DefaultHeaderMapper设置该值。如果未提供该属性且头部映射器未设置,默认值依赖于底层的Spring AMQPMessageProperties转换器被以下机构使用兔子模板. 如果没有自定义,默认是持续. 自选。 |
| 13 | 定义相关数据的表达式。提供后,配置底层AMQP模板以接收发布者确认。需要专用兔子模板以及一个缓存连接工厂其出版社确认属性设置为true. 当收到发布者确认并提供相关数据时,确认会写入确认-确认-通道或者确认-nack-频道,取决于确认类型。确认的有效载荷是该表达式定义的相关数据,消息的“amqp_publishConfirm”头设置为true (啊)或false (纳克). 为纳克实例,一个额外的头部(amqp_publishConfirmNackCause)被提供。 例子:头部['myCorrelationData'],有效载荷. 如果表达式解析为留言<?>实例(例如“#this”),即在啊/纳克通道基于该消息,并添加了额外的头部。另见发布者确认和返回的替代机制。 自选。 |
| 14 | 正向的通道(啊) 发送发布者确认。有效载荷是由确认-相关-表达.
需要基础异步兔子模板拥有其enableConfirms属性设置为true. 另见“发布者确认和返回的替代机制”。可选(默认为零通道). |
| 15 | 自4.2版本起。负面通道(纳克) 发送发布者确认。有效载荷是由确认-相关-表达.
需要基础异步兔子模板拥有其enableConfirms属性设置为true. 另见“发布者确认和返回的替代机制”。可选(默认为零通道). |
| 16 | 设置后,如果发布者确认未在毫秒内收到,网关会合成负向确认(nack)。待处理确认每50%检查一次,因此实际发送nack的时间介于此值的1倍到1.5倍之间。另见发布者确认和返回的替代机制。默认无(nack不会生成)。 |
| 17 | 返回消息发送到的信道。
在提供后,底层的AMQP模板被配置为返回无法投递的消息到网关。
该消息由AMQP接收到的数据构成,并附加以下额外头部:amqp_returnReplyCode,amqp_returnReplyText,amqp_returnExchange和amqp_returnRoutingKey.
需要基础异步兔子模板拥有其命令的属性设置为true.
另见出版商确认与退货的替代机制。
自选。 |
| 18 | 当设置为false,端点在应用上下文初始化期间尝试连接到代理。
这样做可以“快速失败”检测错误配置,通过在代理程序失效时记录错误消息。
什么时候true(默认情况下),连接被建立(如果连接尚未存在,因为有其他组件建立
它)在发送第一条消息时。 |
另请参见异步服务激活器以获取更多信息。
|
兔子模板
当您使用确认和退货时,我们建议您 |
出版商确认与退还的替代机制
当连接工厂配置为发布者确认和返回时,上述章节讨论了消息通道的配置以异步接收确认和返回。 从5.4版本开始,增加了一种通常更容易使用的机制。
此时,不要配置确认-相关-表达或者确认和回传通道。
相反,添加一个相关数据实例在AmqpHeaders.PUBLISH_CONFIRM_CORRELATION页眉;然后你可以通过查看未来的状态来等待结果相关数据你发过消息的实例。
这返回消息字段在未来完成前(如果返回消息)总是会被填充。
CorrelationData corr = new CorrelationData("someId"); // <--- Unique "id" is required for returns
someFlow.getInputChannel().send(MessageBuilder.withPayload("test")
.setHeader("rk", "someKeyThatWontRoute")
.setHeader(AmqpHeaders.PUBLISH_CONFIRM_CORRELATION, corr)
.build());
...
try {
Confirm Confirm = corr.getFuture().get(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
Message returned = corr.getReturnedMessage();
if (returned !- null) {
// message could not be routed
}
}
catch { ... }
为了提升性能,你可能想发送多条消息,然后等确认,而不是一次一条。
返回的消息是转换后的原始消息;你可以对A进行子类相关数据提供你需要的任何额外数据。
入站消息转换
到达通道适配器或网关的入站消息会被转换为春季消息 留言<?>有效载荷使用消息转换器。
默认情况下,简易消息转换器所用的,负责 Java 序列化和文本。
头部通过DefaultHeaderMapper.inboundMapper()默认。
如果发生转换错误且未定义错误通道,异常会抛入容器,由监听器容器的错误处理程序处理。
默认错误处理程序将转换错误视为致命,消息将被拒绝(如果队列配置为死信交换,则会被路由到死信交换)。
如果定义了错误信道,则错误消息有效载荷是ListenerExecutionFailedException具有性质失败消息(无法转换的Spring AMQP消息)以及原因.
如果容器确认模式是自动(默认)且错误流消耗错误而不抛出异常,原始消息将被确认。
如果错误流抛出异常,异常类型与容器的错误处理程序结合,将决定消息是否被重新排队。
如果容器配置为确认模式。手册,有效载荷为ManualAckListenerExecutionFailedException附加性质渠道和配送标签.
这使得错误流能够调用基本的或basicNack(或basicReject)用于控制消息的处理方式。
外发消息转换
春季AMQP 1.4引入了内容类型委托消息转换器,其中实际的转换器是基于
在 incoming content type message 属性上。
这可以被入站端点使用。
从 Spring Integration 4.3 版本开始,你可以使用内容类型委托消息转换器在出站端点上也同样如此,且内容类型头部指示所使用的转换器。
以下示例配置为内容类型委托消息转换器,默认转换器为简易消息转换器(处理Java序列化和纯文本),以及一个JSON转换器:
<amqp:outbound-channel-adapter id="withContentTypeConverter" channel="ctRequestChannel"
exchange-name="someExchange"
routing-key="someKey"
amqp-template="amqpTemplateContentTypeConverter" />
<int:channel id="ctRequestChannel"/>
<rabbit:template id="amqpTemplateContentTypeConverter"
connection-factory="connectionFactory" message-converter="ctConverter" />
<bean id="ctConverter"
class="o.s.amqp.support.converter.ContentTypeDelegatingMessageConverter">
<property name="delegates">
<map>
<entry key="application/json">
<bean class="o.s.amqp.support.converter.Jackson2JsonMessageConverter" />
</entry>
</map>
</property>
</bean>发送消息ct请求频道其中内容类型头部设置为application/json导致选择 JSON 转换器。
这适用于出站通道适配器和网关。
|
从5.0版本开始,添加到 然而,也存在需要之前行为的情况——例如,当 现在有一个名为 从5.1.9版本开始,类似的版本 |
出站用户ID
Spring AMQP 1.6 引入了一种机制,允许为外发消息指定默认用户 ID。
一直以来,设置AmqpHeaders.USER_ID头部,现在优先于默认。
这对给收件人发消息可能很有用。
对于入站消息,如果消息发布者设置了该属性,该属性会在AmqpHeaders.RECEIVED_USER_ID页眉。
请注意,RabbitMQ会验证用户ID是否为连接的实际用户ID,或者连接允许冒充。
要配置出站消息的默认用户ID,请在兔子模板并配置出站适配器或网关使用该模板。
同样,要在回复中设置用户ID属性,向入站网关注入一个配置合适的模板。
更多信息请参见春季AMQP文档。
延迟消息交换
Spring AMQP 支持 RabbitMQ 延迟消息交换插件。
对于入站消息,以下X延迟头部映射到AmqpHeaders.RECEIVED_DELAY页眉。
设置AMQPHeaders.DELAY头部 导致相应的X延迟在外发消息中设置的头部。
你也可以指定延迟和延迟表达式出站端点上的属性(延迟表达式在使用 XML 配置时)。
这些性质优先于AmqpHeaders.DELAY页眉。
AMQP支持的消息频道
有两种消息通道实现。
一个是点对点,另一个是发布-订阅。
这两个通道都为底层的配置属性提供了广泛的Amqp模板和SimpleMessageListenerContainer(如本章前述关于通道适配器和网关的说明所示)。
然而,我们这里展示的例子配置非常有限。
探索XML模式以查看可用的属性。
点对点信道可能如下示例:
<int-amqp:channel id="p2pChannel"/>在盖子下,前述例子导致队列叫si.p2pChannel该通道发送给队列(严格来说,是通过将与该交换机名称匹配的路由密钥发送到无名直接交换机队列).
该信道还注册了一个消费者队列.
如果你希望信道是“可轮询”的,而不是消息驱动的,请提供信息驱动值为false,如下示例所示:
<int-amqp:channel id="p2pPollableChannel" message-driven="false"/>一个发布订阅频道可能如下:
<int-amqp:publish-subscribe-channel id="pubSubChannel"/>在被子里,前面的例子引发了一个名为si.fanout.pub子频道该频道将发送到该扇形交换。
该通道还声明了一个服务器名的专属、自动删除、非持久通道队列并在注册用户时将其绑定到扇出交换机队列接收信息。
发布-订阅-频道没有“可轮询”选项。
它必须是信息驱动的。
从4.1版本开始,AMQP支持的消息通道(配合通道交易) 支持模板通道交易分离事务配置用于摘要MessageListenerContainer和
对于兔子模板.
请注意,之前,通道交易是true默认。
现在,默认情况下,它就是false对于摘要MessageListenerContainer.
在4.3版本之前,AMQP支持的频道仅支持消息序列 化有效载荷和头部。
整个消息被转换(序列化)并发送到 RabbitMQ。
现在,你可以设置提取物-有效载荷属性(或setExtractPayload()使用 Java 配置时)变成true.
当这面旗帜是true,消息有效载荷被转换并映射报头,方式类似于使用通道适配器。
这种安排使得AMQP支持的信道可以与不可序列化的有效载荷一起使用(可能还包括其他消息转换器,例如:Jackson2JsonMessageConverter).
有关默认映射头的更多信息,请参见AMQP消息头。
你可以通过提供使用以下条件的自定义映射器来修改映射出站头映射器和入站头映射器属性。
你现在也可以指定默认投递模式当 没有 时,用于设置传递模式amqp_deliveryMode页眉。
默认情况下,Spring AMQP消息属性使用持续交付模式。
| 与其他持久性支持信道一样,AMQP支持信道旨在提供消息持久性,以避免消息丢失。 它们不打算将工作分发给其他同类应用。 为此,建议使用通道适配器。 |
从5.0版本开始,可轮询通道现在会屏蔽指定轮询线程收到超时(默认为1秒)。
之前,与其他人不同Pollable频道实现中,如果没有消息可用,线程会立即返回调度器,无论接收超时。
定型比用basicGet()为了获取消息(无超时),因为必须创建一个消费者来接收每条消息。
要恢复之前的行为,请设置轮询器的收到超时到0。 |
使用 Java 配置配置
以下示例展示了如何用 Java 配置配置通道:
@Bean
public AmqpChannelFactoryBean pollable(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
AmqpChannelFactoryBean factoryBean = new AmqpChannelFactoryBean();
factoryBean.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory);
factoryBean.setQueueName("foo");
factoryBean.setPubSub(false);
return factoryBean;
}
@Bean
public AmqpChannelFactoryBean messageDriven(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
AmqpChannelFactoryBean factoryBean = new AmqpChannelFactoryBean(true);
factoryBean.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory);
factoryBean.setQueueName("bar");
factoryBean.setPubSub(false);
return factoryBean;
}
@Bean
public AmqpChannelFactoryBean pubSub(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
AmqpChannelFactoryBean factoryBean = new AmqpChannelFactoryBean(true);
factoryBean.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory);
factoryBean.setQueueName("baz");
factoryBean.setPubSub(false);
return factoryBean;
}
使用 Java DSL 配置
以下示例展示了如何使用Java DSL配置信道:
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow pollableInFlow(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
return IntegrationFlow.from(...)
...
.channel(Amqp.pollableChannel(connectionFactory)
.queueName("foo"))
...
.get();
}
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow messageDrivenInFow(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
return IntegrationFlow.from(...)
...
.channel(Amqp.channel(connectionFactory)
.queueName("bar"))
...
.get();
}
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow pubSubInFlow(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
return IntegrationFlow.from(...)
...
.channel(Amqp.publishSubscribeChannel(connectionFactory)
.queueName("baz"))
...
.get();
}
AMQP 消息头
概述
Spring Integration 的 AMQP 适配器会自动映射所有 AMQP 属性和头部。
(这与4.3版本不同——之前只映射标准头部。)
默认情况下,这些属性会被复制到Spring Integration之间消息头通过使用DefaultAmqpHeaderMapper.
你可以上传你自己的 AMQP 专用头部映射器实现,因为适配器本身有支持此功能的属性。
AMQP 内任何用户自定义的头部消息属性除非被请求首部名称或回复头名称的性质DefaultAmqpHeaderMapper.
默认情况下,对于出站映射器来说,不行x-*头部是映射的。
请参见本节后面的警告部分。
要覆盖默认并恢复到4.3之前的行为,请使用STANDARD_REQUEST_HEADERS和STANDARD_REPLY_HEADERS在地产中。
在映射用户自定义的头部时,值也可以包含简单的万用符模式(例如东西*或*东西)以匹配。
所有标题都匹配。* |
从4.1版本开始,抽象首部映射器(aDefaultAmqpHeaderMapper超类)令NON_STANDARD_HEADERSTokens配置为请求首部名称和回复头名称性质(除了现有的STANDARD_REQUEST_HEADERS和STANDARD_REPLY_HEADERS)用于映射所有用户自定义的头部。
这org.springframework.amqp.support.AmqpHeaders类识别由DefaultAmqpHeaderMapper:
-
amqp_appId -
amqp_clusterId -
amqp_contentEncoding -
amqp_contentLength -
内容类型(参见这内容类型页眉) -
amqp_correlationId -
amqp_delay -
amqp_deliveryMode -
amqp_deliveryTag -
amqp_expiration -
amqp_messageCount -
amqp_messageId -
amqp_receivedDelay -
amqp_receivedDeliveryMode -
amqp_receivedExchange -
amqp_receivedRoutingKey -
amqp_redelivered -
amqp_replyTo -
amqp_timestamp -
amqp_type -
amqp_userId -
amqp_publishConfirm -
amqp_publishConfirmNackCause -
amqp_returnReplyCode -
amqp_returnReplyText -
amqp_returnExchange -
amqp_returnRoutingKey -
amqp_channel -
amqp_consumerTag -
amqp_consumerQueue
如本节前文所述,使用该模式的头部映射模式是复制所有头部的常见方式。
然而,这可能会带来一些意想不到的副作用,因为某些RabbitMQ专有属性/头部也会被复制。
例如,使用联合时,收到的消息可能有一个属性命名*x-接收-from(接收),包含发送消息的节点。
如果你在入站网关的请求和回复头映射中使用通配字符,这个头部会被复制,这可能会引发Federation化时的一些问题。
该回复消息可能会被联合回发送中介,发送代理可能认为消息在循环,从而悄无声息地丢弃消息。
如果你想利用万用符头映射的便利性,可能需要在下游流程中过滤掉一些头部。
例如,为了避免复制*x-接收-from(接收)标题返回你可以使用的回复<int:header-filter ...header-names=“x-received-from”>然后再将回复发送到AMQP入站网关。
或者,你也可以明确列出那些你真正想映射的属性,而不是使用万能符。
因此,对于入站消息,映射器默认不会映射任何x-*头。
它也不会映射传递模式前往amqp_deliveryMode以避免该头从入站消息传播到出站消息。
相反,该头部映射为amqp_receivedDeliveryMode,该映射不映射到输出。 |
从4.3版本开始,头部映射中的模式可以通过在模式前加上!.
否定模式优先级,因此列表如STANDARD_REQUEST_HEADERS,thing1,ba*,!thing2,!thing3,qux,!thing1不映射东西1(nor东西2也不东西3).
标准头部 plus坏和库克斯被映射。
否定技术可以很有用,例如当接收端下游以不同方式进行JSON反序列化逻辑时,不映射JSON类型头部用于接收消息。
为此,一个!json_*应配置为入站通道适配器/网关的头部映射器。
如果你有一个用户自定义的头部,开头是!你想要映射的,需要用 转义,具体如下:\STANDARD_REQUEST_HEADERS,\!我的爆炸头.
该头!我的BangHeader现已绘制。 |
从5.1版本开始,DefaultAmqpHeaderMapper将退回映射MessageHeaders.ID和消息头部.时间戳自MessageProperties.messageId和MessageProperties.timestamp分别,如果对应的amqp_messageId或amqp_timestamp发件消息中不存在头部。
入站属性将映射到amqp_*标题和以前一样。
填充messageId(信息ID当消息消费者使用有状态重试时,属性。 |
这内容类型页眉
与其他头部不同,AmqpHeaders.CONTENT_TYPE前没有amqp_;这使得 contentType 头部在不同技术间实现透明传递。
例如,发送到RabbitMQ队列的入站HTTP消息。
这内容类型头部映射到春季AMQP的MessageProperties.contentType属性随后被映射到 RabbitMQ 的content_type财产。
在5.1版本之前,该头部也被映射为MessageProperties.headers地图;这是错误的,而且该值可能错误,因为底层的Spring AMQP消息转换器可能更改了内容类型。
这种变化将在一级舱中体现出来content_type属性,但不在RabbitMQ头部映射中。
入站映射忽略了头部的映射值。内容类型不再映射到头部映射中的某个条目。
严格消息顺序
本节描述了进站和出站消息的消息排序。
入境
如果你需要严格排序入站消息,必须配置入站监听器容器预取计数属性到1.
这是因为如果消息失败并被重新投递,它会在已有预取消息之后到达。
自 Spring AMQP 2.0 版本起,预取计数默认为250以提升性能。
严格的订购要求以性能下降为代价。
出境
考虑以下积分流程:
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow flow(RabbitTemplate template) {
return IntegrationFlow.from(Gateway.class)
.split(s -> s.delimiters(","))
.<String, String>transform(String::toUpperCase)
.handle(Amqp.outboundAdapter(template).routingKey("rk"))
.get();
}
假设我们发消息一个,B和C通往门户。
虽然信息很可能存在一个,B,C按顺序发送,没有保证。
这是因为模板每次发送作都会“借用”缓存中的通道,且不能保证每个消息都使用相同的通道。
一种解决方案是在分路器之前启动事务,但RabbitMQ中的事务成本高昂,性能可能会降低数百倍。
为了更高效地解决这个问题,从 5.1 版本开始,Spring Integration 提供了BoundRabbit频道建议即HandleMessageAdvice.
参见“处理消息建议”。
在分路器之前应用时,确保所有下游作都在同一通道上进行,并且可选地等待所有发送消息的发布者确认(如果连接工厂已配置为确认信息)。
以下示例展示了如何使用BoundRabbit频道建议:
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow flow(RabbitTemplate template) {
return IntegrationFlow.from(Gateway.class)
.split(s -> s.delimiters(",")
.advice(new BoundRabbitChannelAdvice(template, Duration.ofSeconds(10))))
.<String, String>transform(String::toUpperCase)
.handle(Amqp.outboundAdapter(template).routingKey("rk"))
.get();
}
注意,同样如此兔子模板(实现了兔子行动)被用于建议和出站适配器。
建议在模板内运行下游流程调用方法使所有作在同一通道上运行。
如果提供了可选的超时,当流程完成时,建议调用等待确认或死亡该方法,如果确认未在指定时间内收到,则抛出异常。
下游流动中不能有线缆的放手(队列通道,执行者频道,以及其他。 |
AMQP采样
想尝试 AMQP 适配器,可以查看 Spring Integration 示例 git 仓库中的示例,链接 https://github.com/SpringSource/spring-integration-samples
目前,有一个示例通过使用出站通道适配器和一个入站通道适配器,演示了Spring Integration AMQP适配器的基本功能。 由于示例中的AMQP代理实现使用RabbitMQ。
| 为了运行这个示例,你需要一个正在运行的RabbitMQ实例。 本地安装,只用基本默认设置就足够了。 有关详细的RabbitMQ安装流程,请参见 https://www.rabbitmq.com/install.html |
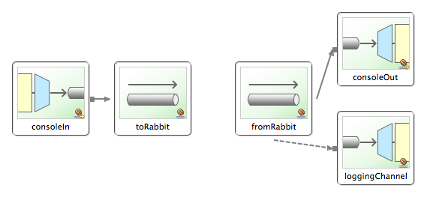
一旦示例应用程序启动,在命令提示符上输入文本,包含该文本的消息会被发送到AMQP队列。 作为交换,Spring Integration 会检索该消息并打印到控制台。
下图展示了本示例中使用的基本 Spring Integration 组件集:
RabbitMQ 流队列支持
6.0版本引入了对RabbitMQ流队列的支持。
这些端点的DSL工厂类为兔子流.
RabbitMQ 流入信道适配器
@Bean
IntegrationFlow simpleStream(Environment env) {
return IntegrationFlow.from(RabbitStream.inboundAdapter(env).streamName("my.stream"))
// ...
.get();
}
@Bean
IntegrationFlow superStream(Environment env) {
return IntegrationFlow.from(RabbitStream.inboundAdapter(env).superStream("my.super.stream", "my.consumer"))
// ...
.get();
}